온라인 해킹 대회 사이트 만들기 3 > AOP를 활용해보자
AOP를 활용한 로깅 시스템 구현
왜 AOP를 사용했는가?
대회 플랫폼은 부정행위 파악등을 위해 로깅시스템이 구현되어야 한다.
만약에 어드민페이지에 대한 모든 로그를 남기는 것을 코드로 짜보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
// 모든 회원들의 리스트를 가져오는 메서드
@GetMapping("")
public AccountDto.Res.AccountList accountViewMapping(@PageableDefault(size = 30, sort = "id", direction = Sort.Direction.DESC) Pageable pageable) {
...
(로깅 로직)
...
return accountService.getAllAccount(pageable);
}
// 회원 추가 메서드
@PostMapping("")
public AccountDto.Res.Signup signupMapping(AccountDto.Req.Signup signup) {
...
(로깅 로직)
...
return accountService.signup(signup);
}
이런식으로 짤 수 있다.
하지만 어드민페이지는 모든 데이터의 CRUD를 다루기 때문에 메서드가 많다.
따라서 아래 코드 처럼 로깅 로직이라는 보일러 플레이트 가 많이 생길 수 밖에 없다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
// 모든 회원들의 리스트를 가져오는 메서드
@GetMapping("")
public AccountDto.Res.AccountList accountViewMapping(@PageableDefault(size = 30, sort = "id", direction = Sort.Direction.DESC) Pageable pageable) {
...
(로깅 로직)
...
return accountService.getAllAccount(pageable);
}
// 회원 추가 메서드
@PostMapping("")
public AccountDto.Res.Signup signupMapping(AccountDto.Req.Signup signup) {
...
(로깅 로직)
...
return accountService.signup(signup);
}
// 회원 수정 메서드
@PatchMapping("{id}")
public Account accountEditMapping(@PathVariable final Long id, AccountDto.Req.SignupWithoutValid editInfo) {
try {
...
(로깅 로직)
...
return accountService.editAccountPartly(id, editInfo);
} catch (DataIntegrityViolationException e){
// mysql Unique 값 설정에 의해 생기는 오류
throw new CustomException(ErrorCode.DUPLICATE_INFORMATION);
}}
// 알림 생성 메서드
@PostMapping("")
public ResponseEntity<String> makeNotificationMapping(NotificationDto.Req req){
...
(로깅 로직)
...
adminNotificationService.makeNotification(req);
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
....
......
(후략)
........
이러한 중복 코드를 생산하고 관리하는 것은 매우 번거로운 일이다.
그래서 AOP를 사용하기로 한다.
구현하며 알아보는 AOP
Aspect Oriented Programming는 직역하면 관점 지향 프로그래밍이다.
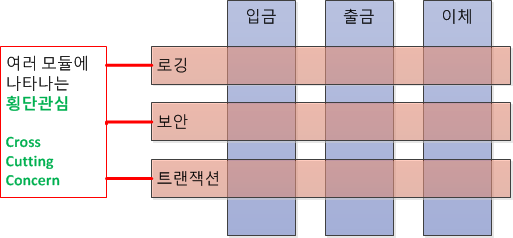
만약 은행에서 입금 출금 이체를 한다면,
각각의 입금 출금 이체에는 로깅, 보안, 등등의 공통 수행 부분이 존재할 것이다. 우리는 이러한 로깅, 보안 등을 관심사라고 부른다.
이러한 공통 수행 부분을 하나의 장소에서 관리할 수 있게 해주는것이 AOP이다.
또한 AOP를 적용한다면,
이체에는 로깅과 같은 다른 부가적인 부분에 신경 쓸 필요없이 오로직 이체 관련 기능에만 집중하면 된다.
아까 위에서 봤던 코드를 그림으로 그려보면 다음과 같다. 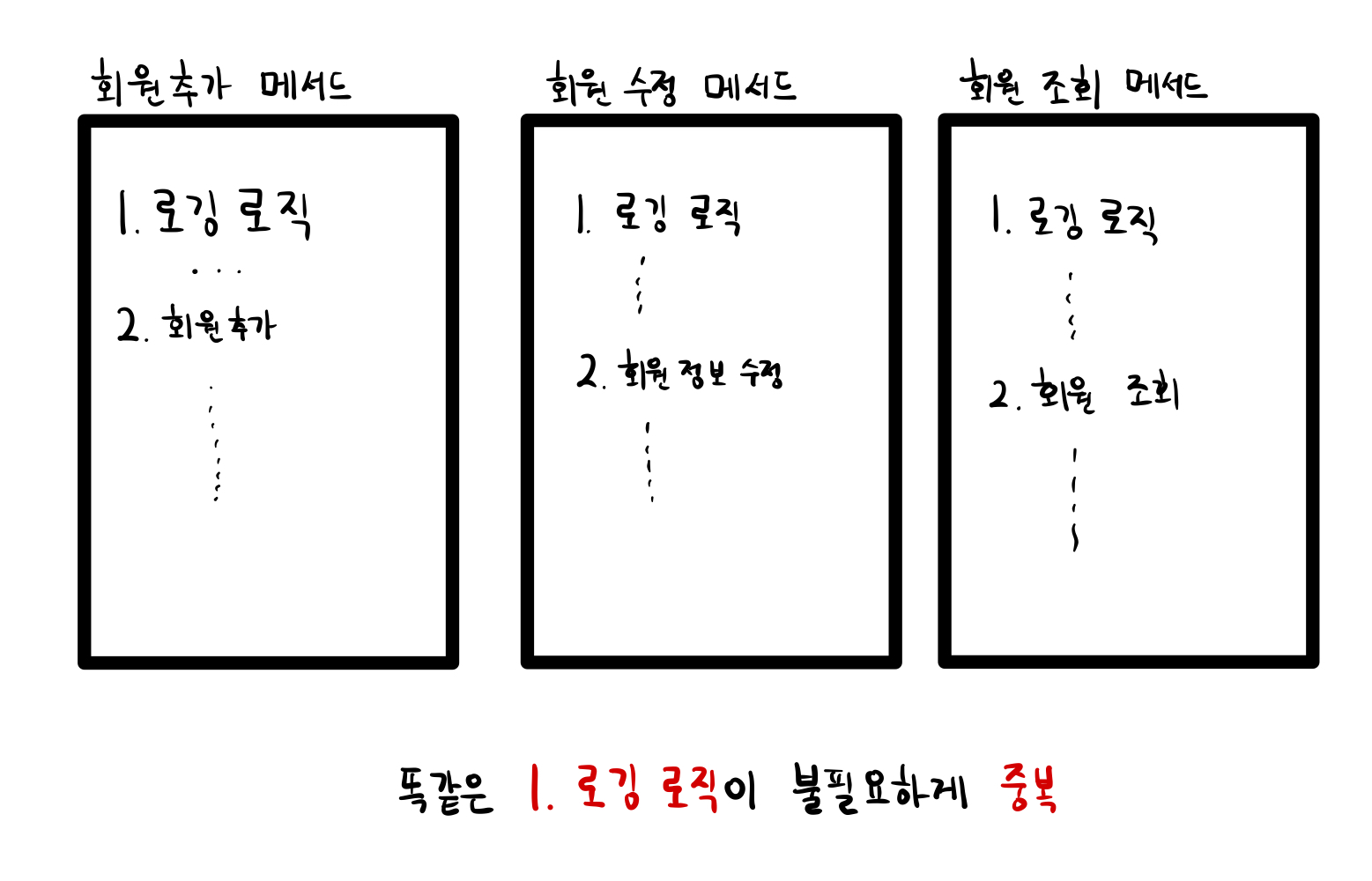
똑같은 1. 로깅로직이 불필요하게 중복된다.
하지만 AOP를 접목하면 다음과 같이 보일러 플레이트를 줄일 수 있다. 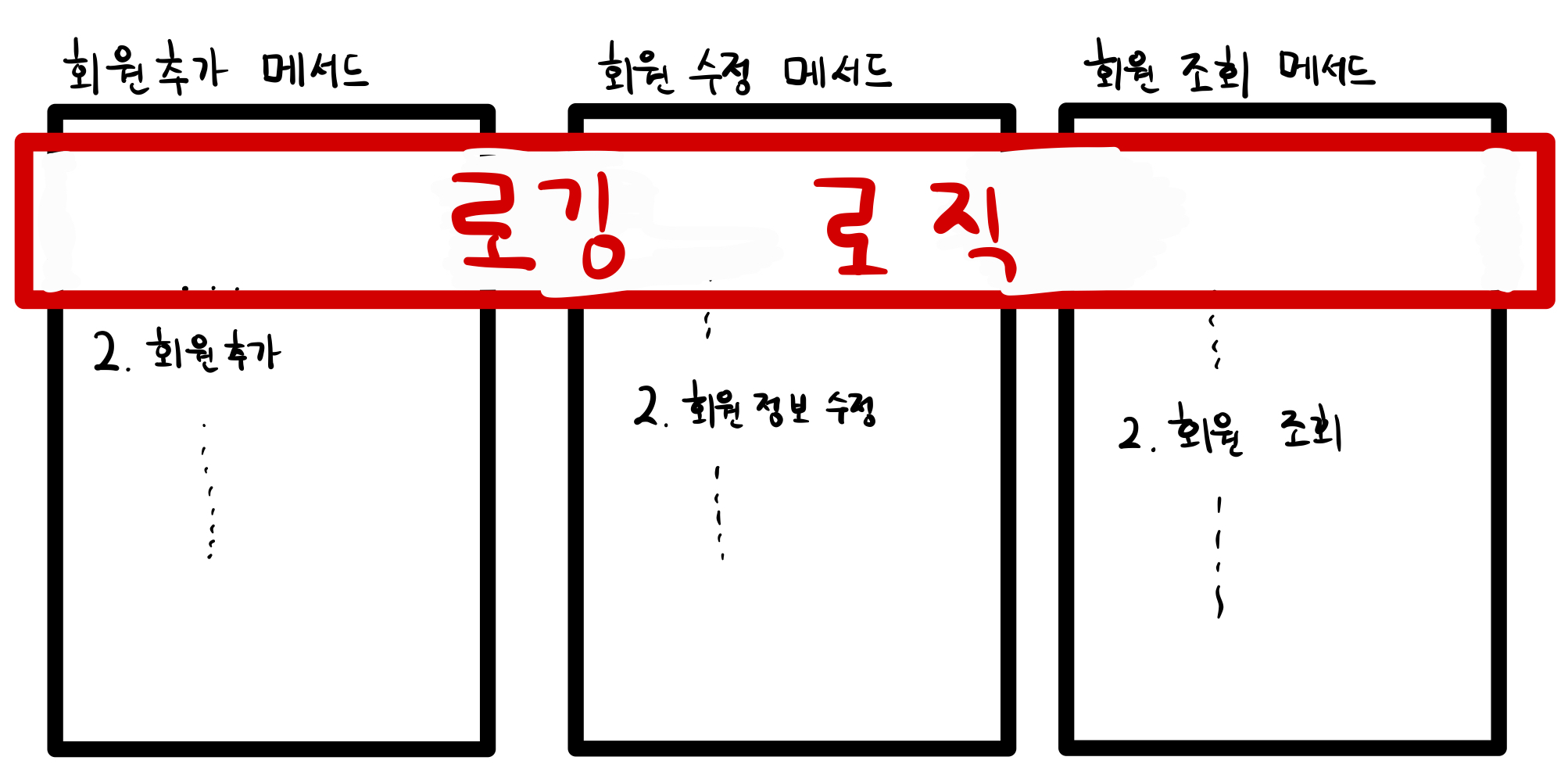 실제로 우리의 IDE창에서 로깅 로직은 한번만 작성하면 되는 것이다.
실제로 우리의 IDE창에서 로깅 로직은 한번만 작성하면 되는 것이다.
이런식으로 AOP는 프로그램 구조에 대한 또 다른 사고 방식을 제공하여 OOP(객체지향 프로그래밍)을 보완한다. OOP에서 모듈의 핵심단위는 클래스이지만, AOP는 그의 단위가 관심사인 것이다.
코딩해보자!
프로젝트 생성, 종속성 등은 생략한다.
일단 첫번째로 간단하게 Admin 메서드에 접근할때, 로그를 남겨보려고 한다.
일단 클래스를 하나 만들어주자.
1
2
3
public class AdminLogAOP {
}
일단 AOP를 사용하려면, @Aspect를 추가하고, 빈에 등록하기 위해 @Component도 추가해준다.
1
2
3
4
5
@Aspect
@Component
public class AdminLogAOP {
}
로그를 남기는 메서드를 만든다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
@Aspect
@Component
public class AdminLogAOP {
public void afterAccessAdminPath(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// 로그를 남긴다.
}
}
이제 이 메서드가 언제 동작할건지 지정해주기 위해 Advice를 작성해야 한다. 작성할 수 있는 Advice는 다음과 같다.
- Before advice
- After returning advice
- After throwing advice
- After (finally) advice
- Around advice
AdminController에서 API가 정상 return 된 후에 로그를 남기면 되기 때문에, After returning advice를 사용할 것이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
@Aspect
@Component
public class AdminLogAOP {
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "execution(* com.penekhun.ctfjserver.Admin.Controller.*.*(..))" )
public void afterAccessAdminPath() {
// 로그를 남긴다.
}
}
이렇게 작성하게 되면, com.penekhun.ctfjserver.Admin.Controller 패키지 내 모든 메서드에서 리턴될때 afterAccessAdminPath메서드가 동작하게 된다.
하지만, 관리자 기능중에서도 로그를 하지 않았으면 하는 메서드가 있을수도 있다.
따라서 그런것들은 AOP메서드에서 JoinPoint를 인자로 받아서, 호출 메서드 이름으로 필터링해주었다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
@Aspect
@Component
public class AdminLogAOP {
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "execution(* com.penekhun.ctfjserver.Admin.Controller.*.*(..))" )
public void afterAccessAdminPath() {
String caller = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
String lowerCase = caller.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (!(lowerCase.contains("log")) || (lowerCase.contains("listmap")) || (lowerCase.contains("download"))) {
logService.logAdminAccess(joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
}
}
Comments powered by Disqus.